Protect advanced machinery
Service machines in time by detecting unsual machine temperatures earlier.
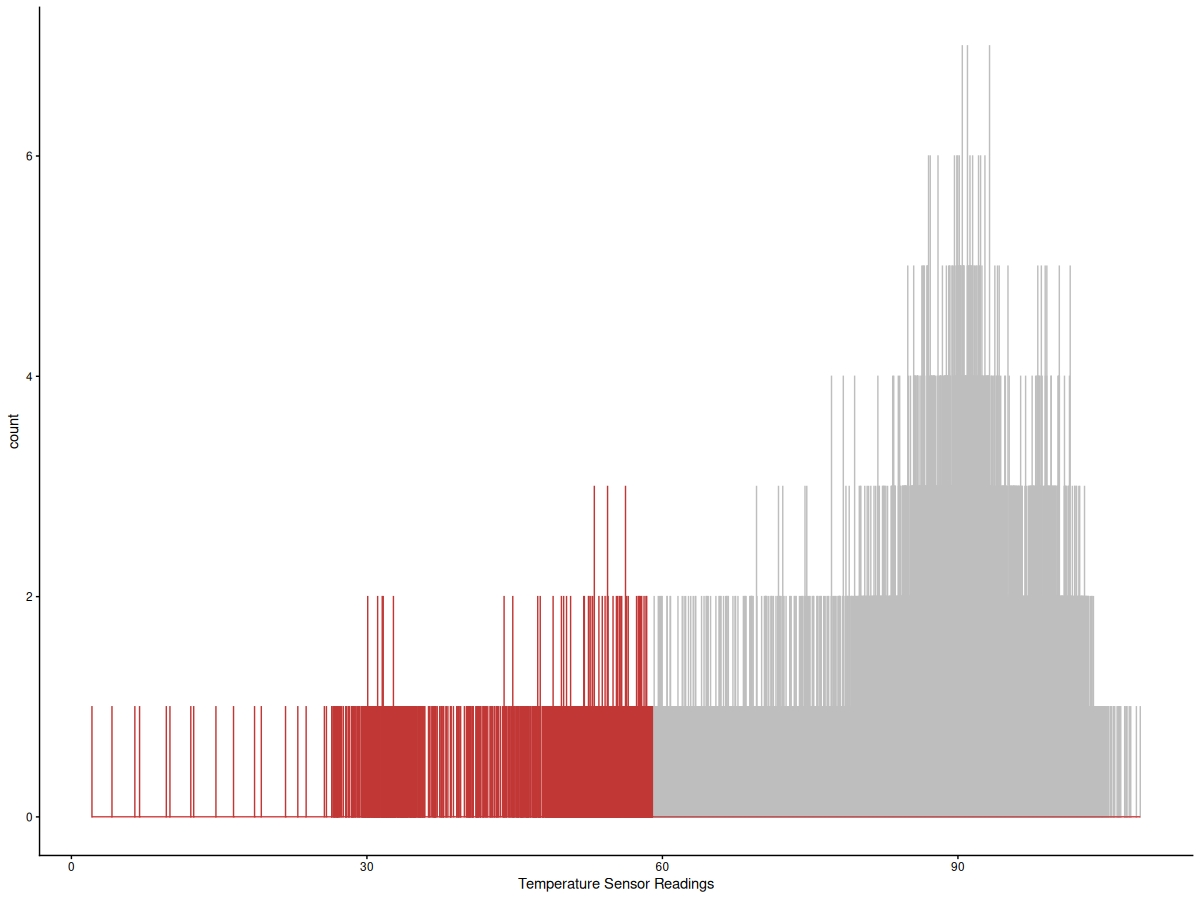

Irregularities in machine sensor data can indicate defects in the machinery.
Detect outliers to prevent equipment failure, improve maintenance efficiency, or improve onsite safety.
The example data is 22,695 temperature sensor readings from an internal component of a large industrial machine, sourced from the Numenta Anomaly Benchmark series.
The dataset includes a planned shutdown and a second unplanned anomaly leading directly to the third anomaly, a catastrophic failure of the machine.
Use SciMi DetectOutliers to monitor machine internal temperatures and instantly find shutdowns and potential risks of failure.
DetectOutliers sends a signal each time an anomaly is detected.
DetectOutliers found three sets of sensor readings with an unusually low temperature. Each set of increasingly frequent outlier temperatures provides an early warning of maintenance shutdown or catastrophic failure.
Recommended action: Investigate the causes of the temperature anomalies to avoid catastrophic failure of the machine.

DetectOutliers found an increasing pattern of outliers on a minute-to-minute basis, demonstrating the imminent breakdown of the machine.
Using the API, the machine can be shut down and serviced before irreparable damage occurs.